In today’s competitive business landscape, optimizing processes is no longer optional—it’s essential. Two of the most popular methodologies for process improvement are Lean and Six Sigma. While both aim to enhance operational efficiency, they take different approaches. This guide explores their differences, benefits, and how to determine which method suits your business.
Understanding Lean and Six Sigma
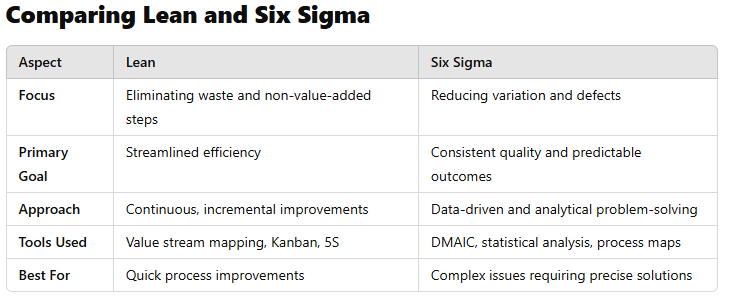
What is Lean?
Lean is a methodology focused on eliminating waste and maximizing value in business processes. Developed from Toyota’s production system, Lean emphasizes continuous improvement (Kaizen) and efficient resource use.
Core Principles of Lean:
- Identify value from the customer’s perspective
- Map the value stream to eliminate non-essential steps
- Create smooth workflows to minimize bottlenecks
- Empower employees to identify and resolve inefficiencies
- Continuously refine processes to sustain improvement
Key Benefits of Lean:
- Reduces unnecessary costs
- Enhances customer satisfaction by delivering faster results
- Improves team collaboration and morale
-
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach designed to improve processes by reducing variation and eliminating defects. Originating at Motorola, Six Sigma uses statistical analysis to achieve near-perfect quality control.
Core Concepts of Six Sigma:
- DMAIC Framework: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control
- Focus on measurable and repeatable improvements
- Reduce process variability to achieve consistent outcomes
Key Benefits of Six Sigma:
- Improves product/service quality
- Reduces error rates and operational risks
- Provides a structured and measurable improvement process
Which Method is Right for Your Business?
When to Choose Lean:
- You face excessive waste or bottlenecks in your processes.
- Speed and efficiency are more critical than perfection.
- Your team is ready to adopt a collaborative, customer-focused mindset.
Example Use Case: A bakery struggling with long production times and inventory waste adopts Lean principles to streamline workflows and improve delivery speed.
When to Choose Six Sigma:
- Your business needs to reduce errors and ensure high-quality outputs.
- Processes are highly complex or prone to variability.
- You want measurable, data-backed improvement strategies.
Example Use Case: A healthcare provider uses Six Sigma to reduce patient waiting times and eliminate billing errors, enhancing customer satisfaction.
When to Use Both (Lean Six Sigma):
Lean and Six Sigma are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many organizations combine them for a holistic approach to process improvement. Lean Six Sigma leverages Lean’s efficiency focus with Six Sigma’s precision, achieving both speed and quality.
Example Use Case: A manufacturing company integrates Lean Six Sigma to reduce defects in production while cutting down lead times.
Steps to Implement Lean or Six Sigma
1. Assess Your Current Processes
- Conduct a workflow audit to identify inefficiencies or defects.
- Collect relevant data to understand process performance.
2. Define Goals and Metrics
- Clearly outline what you want to achieve (e.g., faster delivery times, reduced errors).
- Set measurable KPIs to track progress.
3. Train Your Team
- Provide Lean or Six Sigma training to employees.
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement and problem-solving.
4. Execute Improvements
- For Lean: Focus on removing non-essential steps and streamlining workflows.
- For Six Sigma: Use DMAIC to identify root causes and implement changes.
5. Monitor and Refine
- Continuously measure results and adjust strategies as needed.
- Use dashboards and reports to track success metrics.
Case Studies: Lean and Six Sigma in Action
Lean Success Story
A retail chain implemented Lean to reduce stock inventory waste. By introducing just-in-time inventory practices and improving communication with suppliers, they saved 20% in inventory costs.
Six Sigma Success Story
A telecommunications company used Six Sigma to identify and resolve recurring network outages. By analyzing data and addressing root causes, they improved service reliability by 35%.
Conclusion
Both Lean and Six Sigma offer powerful tools for improving business processes, but the right choice depends on your organization’s unique challenges and goals. Lean is ideal for eliminating waste and speeding up workflows, while Six Sigma excels in achieving consistent quality and reducing errors.
For businesses looking for the best of both worlds, Lean Six Sigma provides a comprehensive framework for sustained success.
Want to optimize your processes? Contact NOJPoint today and discover how our experts can help you implement Lean, Six Sigma, or both to achieve operational excellence.
